A line consists of two points: a start point and an endpoint. A series of lines can be connected, but each segment is considered a separate line entity.
![]() Surveying different methods for drawing lines in gCADPlus landscape design software
Surveying different methods for drawing lines in gCADPlus landscape design software
To draw a line
Do one of the following:
Choose Draw > Line from the Draw drop-down menu.
On a toolbar, click the Line tool.
Type the full-text word line and then press Enter
Type the L shortcut and press Enter
Specify the start point.
Specify the endpoint.
Hit enter or right-click to finish.
Coordinate entry
In gCADPlus, when a command, such as LINE, prompts for a point, you can use the pointing device (your mouse) to specify a point by clicking or entering a coordinate value on the command line. Coordinates may be entered as either Cartesian or polar coordinates.
Cartesian coordinates
A Cartesian coordinate system has three axes, X, Y, and Z. When you enter coordinate values; you indicate a point’s distance (in units) and its direction (+ or -) along the X, Y, and Z axes relative to the coordinate system’s point of origin where all coordinate values are zero (0,0,0). Negative values on the X plane are to the left of the point of origin, and positive values on the X plane are to the right. Negative values on the Y plane are below the point of origin, and positive values on the Y plane are above them.
Entering Cartesian coordinates
To use a coordinate to specify a point, enter an X value and a Y value separated by a comma (X,Y). gCADPlus does not require using the 3rd dimension, so it can be ignored even though a value for the Z plane will be 0 – the coordinate set will appear as: (X,Y,Z). The X value is the positive or negative distance, in units, along the horizontal axis. The Y value is the positive or negative distance, in units, along the vertical axis.
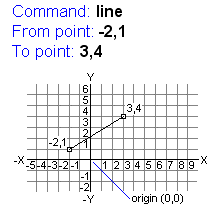
Absolute coordinate values are based on the origin (0,0), where the X and Y axes intersect. When you know the point coordinate’s precise X and Y values, use an absolute coordinate. For example, the coordinate 3,4 specifies a point 3 units along the X axis and four units along the Y axis from the origin.
Relative coordinate values are based on the last point entered. Use a relative coordinate when you know the position of a point relative to the previous point. To specify a relative coordinate, precede the coordinate with an @ symbol. For example, the coordinate @3,4 specifies a point of 3 units along the X-axis and four units along the Y-axis from the last point selected.
The example at right draws a line beginning at a point with an X value of -2, a Y value of 1, and an endpoint at 3,4. Pressing ENTER at the To Point prompt ends the command.
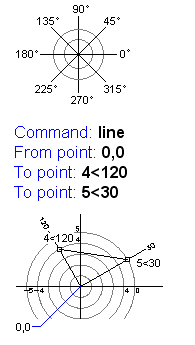
Polar coordinates
Polar coordinates use a distance and a fixed angle to locate a point.

With Cartesian and polar coordinates, you can enter absolute coordinates based on the point of origin (0,0,0), or relative coordinates based on the last point specified.